Aditya Pradhan, Sarala Khaling
Tropical Ecology | February 27, 2024
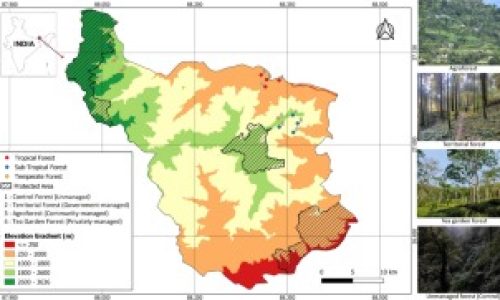
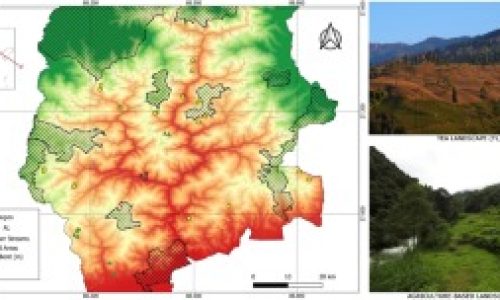
In the socio-ecological landscapes of tropical mountains, including the highly diverse Eastern Himalaya, fragments of natural forests have been traditionally managed as part of different agriculture systems. Recent studies have recognized their role as important biodiversity repositories outside protected areas. However, basic information on forest structure and composition of these forests outside protected areas is still limited in the Himalaya. In the current study, diversity, structure, composition, and regeneration status of non-protected forests were studied across 15 spatially different sites in the socio-ecological landscapes of Darjeeling-Sikkim, Eastern Himalaya, across an approximate elevation range of 500-2300 m above sea level.