Sara Löfqvist, Fritz Kleinschroth, Adia Bey, Ariane de Bremond, Ruth DeFries, Jinwei Dong, Forrest Fleischman, Sharachchandra Lele, Dominic A Martin, Peter Messerli, Patrick Meyfroidt, Marion Pfeifer, Sarobidy O Rakotonarivo, Navin Ramankutty, Vijay Ramprasad, Pushpendra Rana, Jeanine M Rhemtulla, Casey M Ryan, Ima Célia Guimarães Vieira, Geoff J Wells, Rachael D Garrett
BioScience | December 14, 2022
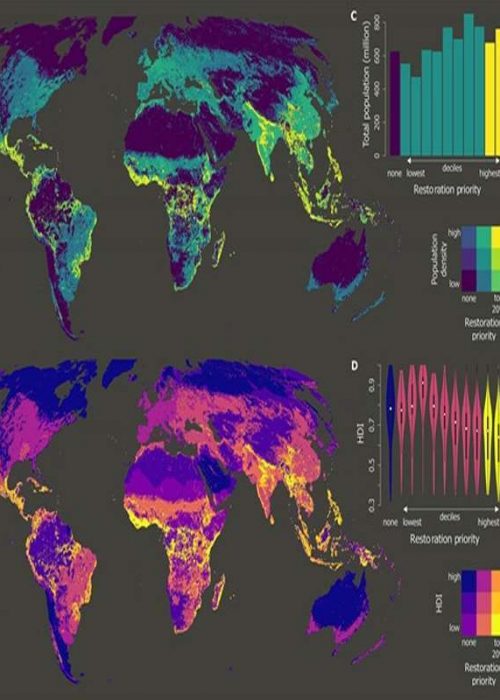
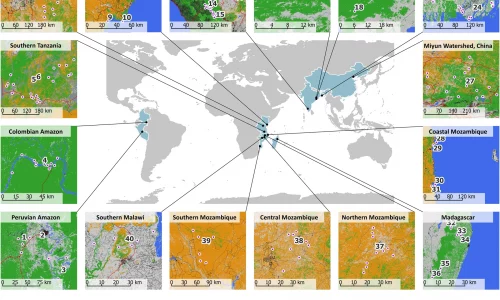
Ecosystem restoration is an important means to address global sustainability challenges. However, scientific and policy discourse often overlooks the social processes that influence the equity and effectiveness of restoration interventions. In the present article, we outline how social processes that are critical to restoration equity and effectiveness can be better incorporated in restoration science and policy. Drawing from existing case studies, we show how projects that align with local people’s preferences and are implemented through inclusive governance are more likely to lead to improved social, ecological, and environmental outcomes.